Class that stores inputs and runs them through the zigzag cost model. More...
Public Member Functions | |
| def | __init__ (self, *Accelerator accelerator, LayerNode layer, SpatialMappingInternal spatial_mapping, SpatialMappingInternal spatial_mapping_int, TemporalMapping temporal_mapping, bool access_same_data_considered_as_no_access=True, float cycles_per_op=1.0) |
| After initialization, the cost model evaluation is run. More... | |
| None | run (self) |
| Run the cost model evaluation. More... | |
| None | calc_memory_utilization (self) |
| None | calc_memory_word_access (self) |
| None | calc_energy (self) |
| Calculates the energy cost of this cost model evaluation by calculating the memory reading/writing energy. More... | |
| None | calc_mac_energy_cost (self) |
| Calculate the dynamic MAC energy. More... | |
| def | calc_memory_energy_cost (self) |
| Computes the memories reading/writing energy by converting the access patterns in self.mapping to energy breakdown using the memory hierarchy of the core on which the layer is mapped. More... | |
| None | calc_latency (self) |
| Calculate latency in 4 steps. More... | |
| None | calc_double_buffer_flag (self) |
| This function checks the double-buffer possibility for each operand at each memory level (minimal memory BW requirement case) by comparing the physical memory size with the effective data size, taking into account the memory sharing between operands. More... | |
| def | calc_allowed_and_real_data_transfer_cycle_per_data_transfer_link (self) |
| Construct a 4-way data transfer pattern for each unit mem, calculate {allowed_mem_updating_cycle, real_data_trans_cycle, DTL_SS_cycle} per period. More... | |
| MemoryAccesses | calculate_real_data_transfer_cycles (self, LayerOperand layer_op, MemoryOperand mem_op, int mem_lvl_id) |
| MemoryAccesses | calculate_allowed_transfer_cycles (self, LayerOperand layer_op, int mem_lv) |
| None | combine_data_transfer_rate_per_physical_port (self) |
| Consider memory sharing and port sharing, combine the data transfer activity Step 1: collect port activity per memory instance per physical memory port Step 2: calculate SS combine and MUW union parameters per physical memory port. More... | |
| list[PortBeginOrEndActivity] | calc_loading_single_port_period_count_1 (self, MemoryPort port, list[tuple[MemoryOperand, int, DataDirection]] mem_op_level_direction_combs, float total_req_bw_aver_computation) |
| Calculate the loading activities for the memory port movement directions with period count of 1. More... | |
| list[PortBeginOrEndActivity] | calc_loading_single_port_period_count_greater_than_1 (self, MemoryPort port, list[tuple[MemoryOperand, int, DataDirection]] mem_op_level_direction_combs) |
| Calculate the loading and offloading activities with mem port movement directions period > 1. More... | |
| def | calc_loading_single_port (self, MemoryPort port) |
| Calculate the loading and offloading activities for a single memory port. More... | |
| def | calc_onloading_combined (self) |
| def | calc_offloading_combined (self) |
| tuple[float, float] | calc_borrowed_loading_cycles_and_bandwidth (self) |
| Calculate the amount of cycles and bandwidth that are borrowed from the computation phase. More... | |
| def | calc_data_loading_latency (self) |
| Calculate the number of data onloading/offloading cycles. More... | |
| None | calc_overall_latency (self) |
| This function integrates the previous calculated SScomb, data loading and off-loading cycle to get the overall latency. More... | |
| FourWayDataMoving[int] | get_inst_bandwidth (self, MemoryLevel memory_level, MemoryOperand memory_operand, float scaling=1) |
| Given a memory level and a memory operand, compute the memory's instantaneous bandwidth required for the memory operand during computation. More... | |
| FourWayDataMoving[int] | get_total_inst_bandwidth (self, MemoryLevel memory_level, float scaling=1) |
| Given a cost model evaluation and a memory level, compute the memory's total instantaneous bandwidth required throughout the execution of the layer that corresponds to this CME. More... | |
| def | __str__ (self) |
| def | __repr__ (self) |
 Public Member Functions inherited from CostModelEvaluationABC Public Member Functions inherited from CostModelEvaluationABC | |
| None | __init__ (self) |
| def | core (self) |
| "CumulativeCME" | __add__ (self, "CostModelEvaluationABC" other) |
| def | __mul__ (self, int number) |
| dict[str, float] | __simplejsonrepr__ (self) |
| Simple JSON representation used for saving this object to a simple json file. More... | |
| def | __jsonrepr__ (self) |
| JSON representation used for saving this object to a json file. More... | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| tuple[list[float], list[float]] | reduce_balanced (list[float] c_list, list[float] m_list, float s) |
| Balance c_list towards minimums m_list with a total maximum reduction of s. More... | |
Detailed Description
Class that stores inputs and runs them through the zigzag cost model.
Initialize the cost model evaluation with the following inputs:
- accelerator: the accelerator that includes the core on which to run the layer
- layer: the layer to run
- spatial_mapping: the spatial mapping
- temporal_mapping: the temporal mapping
From these parameters, the following attributes are computed:
- core: The core on which the layer is ran. This should be specified in the LayerNode attributes.
- mapping: The combined spatial and temporal mapping object where access patterns are computed.
The following cost model attributes are also initialized:
- mem_energy_breakdown: The energy breakdown for all operands
- energy: The total energy
After initialization, the cost model evaluation is run.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ __init__()
| def __init__ | ( | self, | |
| *Accelerator | accelerator, | ||
| LayerNode | layer, | ||
| SpatialMappingInternal | spatial_mapping, | ||
| SpatialMappingInternal | spatial_mapping_int, | ||
| TemporalMapping | temporal_mapping, | ||
| bool | access_same_data_considered_as_no_access = True, |
||
| float | cycles_per_op = 1.0 |
||
| ) |
After initialization, the cost model evaluation is run.
- Parameters
-
accelerator the accelerator that includes the core on which to run the layer the layer to run access_same_data_considered_as_no_access (optional)
Member Function Documentation
◆ __repr__()
| def __repr__ | ( | self | ) |
◆ __str__()
| def __str__ | ( | self | ) |
◆ calc_allowed_and_real_data_transfer_cycle_per_data_transfer_link()
| def calc_allowed_and_real_data_transfer_cycle_per_data_transfer_link | ( | self | ) |
Construct a 4-way data transfer pattern for each unit mem, calculate {allowed_mem_updating_cycle, real_data_trans_cycle, DTL_SS_cycle} per period.
TODO cleanup
◆ calc_borrowed_loading_cycles_and_bandwidth()
| tuple[float, float] calc_borrowed_loading_cycles_and_bandwidth | ( | self | ) |
Calculate the amount of cycles and bandwidth that are borrowed from the computation phase.
◆ calc_data_loading_latency()
| def calc_data_loading_latency | ( | self | ) |
Calculate the number of data onloading/offloading cycles.
This function first gathers the correct cycles per port, then combines them.
◆ calc_double_buffer_flag()
| None calc_double_buffer_flag | ( | self | ) |
This function checks the double-buffer possibility for each operand at each memory level (minimal memory BW requirement case) by comparing the physical memory size with the effective data size, taking into account the memory sharing between operands.

◆ calc_energy()
| None calc_energy | ( | self | ) |
Calculates the energy cost of this cost model evaluation by calculating the memory reading/writing energy.
◆ calc_latency()
| None calc_latency | ( | self | ) |
Calculate latency in 4 steps.
1) As we already calculated the ideal data transfer rate in combined_mapping.py (in the Mapping class), here we start with calculating the required (or allowed) memory updating window by comparing the effective data size with the physical memory size at each level. If the effective data size is smaller than 50% of the physical memory size, then we take the whole period as the allowed memory updating window (double buffer effect); otherwise we take the the period divided by the top_ir_loop as the allowed memory updating window. 2) Then, we compute the real data transfer rate given the actual memory bw per functional port pair, assuming we have enough memory ports. 3) In reality, there is no infinite memory port to use. So, as the second step, we combine the real data transfer attributes per physical memory port. 4) Finally, we combine the stall/slack of each memory port to get the final latency.
Reimplemented in CostModelEvaluationForIMC.
◆ calc_loading_single_port()
| def calc_loading_single_port | ( | self, | |
| MemoryPort | port | ||
| ) |
Calculate the loading and offloading activities for a single memory port.

◆ calc_loading_single_port_period_count_1()
| list[PortBeginOrEndActivity] calc_loading_single_port_period_count_1 | ( | self, | |
| MemoryPort | port, | ||
| list[tuple[MemoryOperand, int, DataDirection]] | mem_op_level_direction_combs, | ||
| float | total_req_bw_aver_computation | ||
| ) |
Calculate the loading activities for the memory port movement directions with period count of 1.

◆ calc_loading_single_port_period_count_greater_than_1()
| list[PortBeginOrEndActivity] calc_loading_single_port_period_count_greater_than_1 | ( | self, | |
| MemoryPort | port, | ||
| list[tuple[MemoryOperand, int, DataDirection]] | mem_op_level_direction_combs | ||
| ) |
Calculate the loading and offloading activities with mem port movement directions period > 1.

◆ calc_mac_energy_cost()
| None calc_mac_energy_cost | ( | self | ) |
Calculate the dynamic MAC energy.
Reimplemented in CostModelEvaluationForIMC.
◆ calc_memory_energy_cost()
| def calc_memory_energy_cost | ( | self | ) |
Computes the memories reading/writing energy by converting the access patterns in self.mapping to energy breakdown using the memory hierarchy of the core on which the layer is mapped.
The energy breakdown is saved in self.mem_energy_breakdown.
The energy total consumption is saved in self.energy_total.
◆ calc_memory_utilization()
| None calc_memory_utilization | ( | self | ) |
◆ calc_memory_word_access()
| None calc_memory_word_access | ( | self | ) |

◆ calc_offloading_combined()
| def calc_offloading_combined | ( | self | ) |
◆ calc_onloading_combined()
| def calc_onloading_combined | ( | self | ) |

◆ calc_overall_latency()
| None calc_overall_latency | ( | self | ) |
This function integrates the previous calculated SScomb, data loading and off-loading cycle to get the overall latency.
- Parameters
-
cycles_per_op cycle counts per mac operand (>1 for bit-serial computation)
◆ calculate_allowed_transfer_cycles()
| MemoryAccesses calculate_allowed_transfer_cycles | ( | self, | |
| LayerOperand | layer_op, | ||
| int | mem_lv | ||
| ) |

◆ calculate_real_data_transfer_cycles()
| MemoryAccesses calculate_real_data_transfer_cycles | ( | self, | |
| LayerOperand | layer_op, | ||
| MemoryOperand | mem_op, | ||
| int | mem_lvl_id | ||
| ) |

◆ combine_data_transfer_rate_per_physical_port()
| None combine_data_transfer_rate_per_physical_port | ( | self | ) |
Consider memory sharing and port sharing, combine the data transfer activity Step 1: collect port activity per memory instance per physical memory port Step 2: calculate SS combine and MUW union parameters per physical memory port.
◆ get_inst_bandwidth()
| FourWayDataMoving[int] get_inst_bandwidth | ( | self, | |
| MemoryLevel | memory_level, | ||
| MemoryOperand | memory_operand, | ||
| float | scaling = 1 |
||
| ) |
Given a memory level and a memory operand, compute the memory's instantaneous bandwidth required for the memory operand during computation.
An additonal scaling factor can be applied to the returned bandwidth NOTE: This function is used in Stream

◆ get_total_inst_bandwidth()
| FourWayDataMoving[int] get_total_inst_bandwidth | ( | self, | |
| MemoryLevel | memory_level, | ||
| float | scaling = 1 |
||
| ) |
Given a cost model evaluation and a memory level, compute the memory's total instantaneous bandwidth required throughout the execution of the layer that corresponds to this CME.
Raises an assertion error if the given memory level is not included in this CME's memory hierarchy. NOTE: this function is used in Stream

◆ reduce_balanced()
|
static |
Balance c_list towards minimums m_list with a total maximum reduction of s.

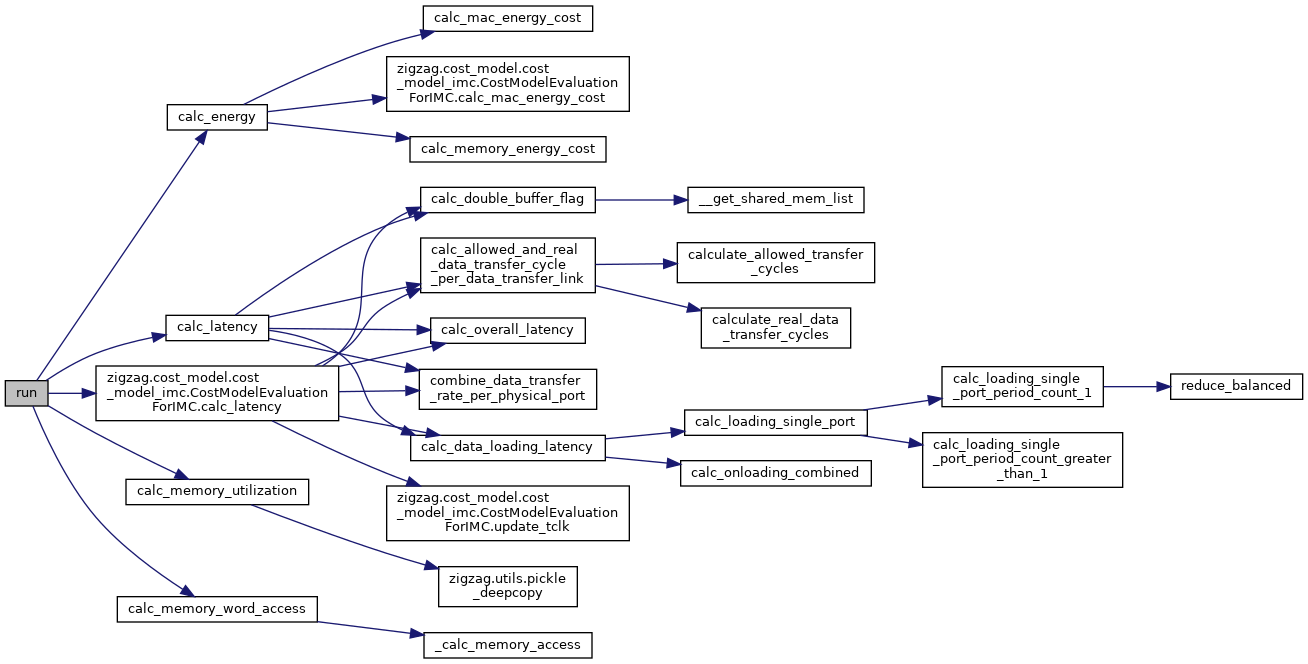
◆ run()
| None run | ( | self | ) |
Run the cost model evaluation.
Reimplemented in CostModelEvaluationForIMC.

Member Data Documentation
◆ accelerator
| accelerator |
◆ access_same_data_considered_as_no_access
| access_same_data_considered_as_no_access |
◆ active_mem_level
| active_mem_level |
◆ allowed_mem_update_cycle
| allowed_mem_update_cycle |
◆ cycles_per_op
| cycles_per_op |
◆ data_loading_cc_pair_combined_per_op
| data_loading_cc_pair_combined_per_op |
◆ data_loading_half_shared_part
| data_loading_half_shared_part |
◆ data_loading_individual_part
| data_loading_individual_part |
◆ data_loading_shared_part
| data_loading_shared_part |
◆ data_offloading_cc_pair_combined
| data_offloading_cc_pair_combined |
◆ data_offloading_cycle
| data_offloading_cycle |
◆ data_onloading_cycle
| data_onloading_cycle |
◆ double_buffer_true
| double_buffer_true |
◆ effective_mem_utili_individual
| effective_mem_utili_individual |
◆ effective_mem_utili_shared
| effective_mem_utili_shared |
◆ ideal_cycle
| ideal_cycle |
◆ ideal_temporal_cycle
| ideal_temporal_cycle |
◆ latency_total0
| latency_total0 |
◆ latency_total1
| latency_total1 |
◆ latency_total2
| latency_total2 |
◆ loading_offloading_bandwidth_borrowed_from_computation
| loading_offloading_bandwidth_borrowed_from_computation |
◆ loading_offloading_cycles_borrowed_from_computation
| loading_offloading_cycles_borrowed_from_computation |
◆ mac_energy
| mac_energy |
◆ mac_spatial_utilization
| mac_spatial_utilization |
◆ mac_utilization0
| mac_utilization0 |
◆ mac_utilization1
| mac_utilization1 |
◆ mac_utilization2
| mac_utilization2 |
◆ mapping
| mapping |
◆ mapping_int
| mapping_int |
◆ mem_energy
| mem_energy |
◆ mem_energy_breakdown
| mem_energy_breakdown |
◆ mem_energy_breakdown_further
| mem_energy_breakdown_further |
◆ mem_hierarchy_dict
| mem_hierarchy_dict |
◆ mem_level_list
| mem_level_list |
◆ mem_sharing_tuple
| mem_sharing_tuple |
◆ mem_size_dict
| mem_size_dict |
◆ mem_updating_window_union_collect
| mem_updating_window_union_collect |
◆ mem_utili_individual
| mem_utili_individual |
◆ mem_utili_shared
| mem_utili_shared |
◆ memory_operand_links
| memory_operand_links |
◆ memory_word_access
| memory_word_access |
◆ port_activity_collect
| port_activity_collect |
◆ real_data_trans_cycle
| real_data_trans_cycle |
◆ spatial_mapping
| spatial_mapping |
◆ spatial_mapping_dict_int
| spatial_mapping_dict_int |
◆ spatial_mapping_int
| spatial_mapping_int |
◆ stall_slack_comb
| stall_slack_comb |
◆ stall_slack_comb_collect
| stall_slack_comb_collect |
◆ temporal_mapping
| temporal_mapping |
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- /home/runner/work/zigzag/zigzag/zigzag/cost_model/cost_model.py